Tertiary Health Care Strategies for Better Outcomes
Breaking Down Tertiary Health Care
Introduction
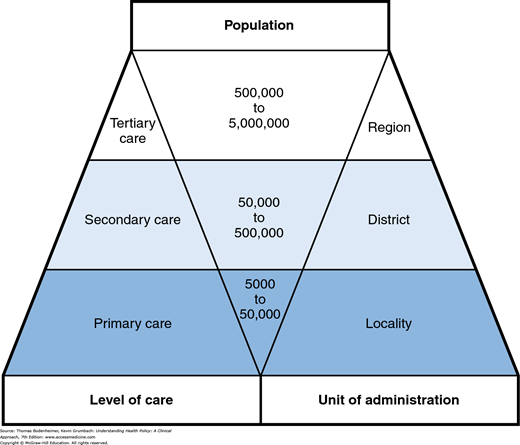
In the realm of healthcare, there exist different levels of care, each serving a specific purpose in addressing patients’ needs. Tertiary health care stands at the top tier, offering specialized services and advanced medical treatments. Let’s delve into what tertiary care entails and how it impacts patient outcomes.
Understanding Tertiary Health Care
Tertiary health care refers to specialized medical care provided by specialists and medical professionals equipped with advanced training and expertise. Unlike primary and secondary care, which focus on preventive and acute care respectively, tertiary care deals with complex medical conditions that often require intensive interventions and specialized equipment.
Scope of Services
Tertiary health care encompasses a wide range of medical specialties and services, including but not limited to cardiology, oncology, neurology, transplant surgery, and intensive care units (ICUs). These services are often provided in specialized hospitals or academic medical centers equipped with state-of-the-art technology and highly skilled medical teams.
Advanced Treatments and Interventions
One of the defining features of tertiary care is its ability to offer advanced treatments and interventions that may not be available at lower levels of care. This includes cutting-edge surgical procedures, experimental therapies, and access to clinical trials for promising new treatments. Tertiary care facilities often serve as hubs for medical research and innovation, driving progress in the field of medicine.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Tertiary health care relies on a multidisciplinary approach, bringing together experts from various medical specialties to collaborate on patient care. This team-based approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care tailored to their specific needs. From diagnosis to treatment and follow-up care, patients benefit from the collective expertise of specialists working together towards a common goal.
Referral System
Access to tertiary health care is typically facilitated through a referral system, with patients being referred by primary care providers or specialists from lower levels of care. This ensures that patients with complex or rare medical conditions are directed to the appropriate specialists and facilities equipped to manage their care effectively. Referral networks play a crucial role in optimizing patient outcomes and minimizing delays in treatment.
Challenges and Considerations
While tertiary health care offers invaluable benefits in terms of specialized expertise and advanced treatments, it also presents challenges and considerations. These may include high costs associated with specialized care, limited accessibility for underserved populations, and potential disparities in access to care based on geographic location or socioeconomic status.
Importance of Tertiary Health Care
Despite its challenges, tertiary health care plays a crucial role in the healthcare ecosystem, serving as a lifeline for patients with complex medical needs. It provides hope and healing for individuals facing challenging diagnoses and offers opportunities for medical breakthroughs that benefit patients worldwide. By investing in tertiary care, healthcare systems can improve patient outcomes, advance medical knowledge, and drive innovation in healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
Tertiary health care represents the pinnacle of medical expertise and innovation, offering specialized services and advanced treatments for patients with complex medical conditions. By understanding the role of
